In Germany, around 400,000 people currently suffer from type 1 diabetes. Of these, around 35,000 children and young adults up to the age of 18 are affected. But what does the diagnosis “type 1 diabetes” actually mean? And what do diabetics need to consider after receiving their diagnosis? Which devices and systems help diabetics to manage their daily lives safely?
Insulin pumps and CGM systems are such aids. Thanks to high-quality frequency components and long-lasting batteries, they function reliably and enable continuous monitoring and insulin delivery. In the following article, you can find out exactly how these instruments for safe diabetes management work and what diabetics need to consider after receiving their diagnosis:
Diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
In people with type 1 diabetes, insulin production in the pancreas is impaired:
Blood sugar regulation:
Insulin is required to transport sugar from the blood into the body’s cells, where it is converted into energy. Without enough insulin, the sugar remains in the blood and leads to increased blood sugar levels.
Symptoms and consequences:
High blood sugar levels can cause various symptoms, such as frequent urination, a strong feeling of thirst, tiredness, nausea and dizziness. In extreme cases, this can lead to loss of consciousness or a diabetic coma.
Treatment:
People with type 1 diabetes have to inject insulin every day to regulate their blood sugar levels and avoid complications.
Forms of treatment
- 1. Intensified Conventional Therapy (ICT)
With ICT, long-acting insulin is injected once or twice a day to cover basic needs. In addition, short-acting insulin is injected before meals to compensate for blood sugar rises after eating or to correct short-term elevated values.
- 2. Insulin Pump Therapy (CSII – continuous subcutaneous insulin injection)
Insulin pump therapy is also known as continuous subcutaneous insulin injection (CSII). The use of an insulin pump has several advantages, including the elimination of frequent injections of insulin.
This therapy uses a small device that is worn on the body and continuously delivers insulin into the subcutaneous fatty tissue. The amount of insulin delivered can be adjusted individually and the user can release additional insulin as required, for example at mealtimes. Insulin pumps can make everyday life easier, especially for people with type 1 diabetes, and are often used in children after diagnosis.
Two different types of devices can be used for insulin pump therapy:
- 2.1. Classic insulin pump
This pump, about the size of a pack of tissues, delivers insulin via a thin tube (catheter) and a needle (cannula). It can be attached to your belt or waistband, put in your trouser pocket or tied around your stomach with a special belt.
- 2.2. Patch-Pumpe
This system is attached directly to the abdomen without a tube and can be controlled with a remote control. The patch system is completely replaced every three days for reasons of hygiene and infection control.
Insulin therapy with an insulin pump is particularly suitable for diabetics who have to receive insulin from outside and for whom insulin administration cannot be guaranteed regularly or independently for various reasons. Insulin pumps are particularly common in children with type 1 diabetes. Insulin pump treatment can also be useful in the following cases:
– Sharp rise in blood sugar in the early morning (dawn phenomenon)
– Frequently occurring low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
– Shift workers
– People with an irregular daily rhythm
– People who cannot eat meals during work without problems.
Successful diabetes treatment: blood glucose monitoring with CGM as a basic requirement
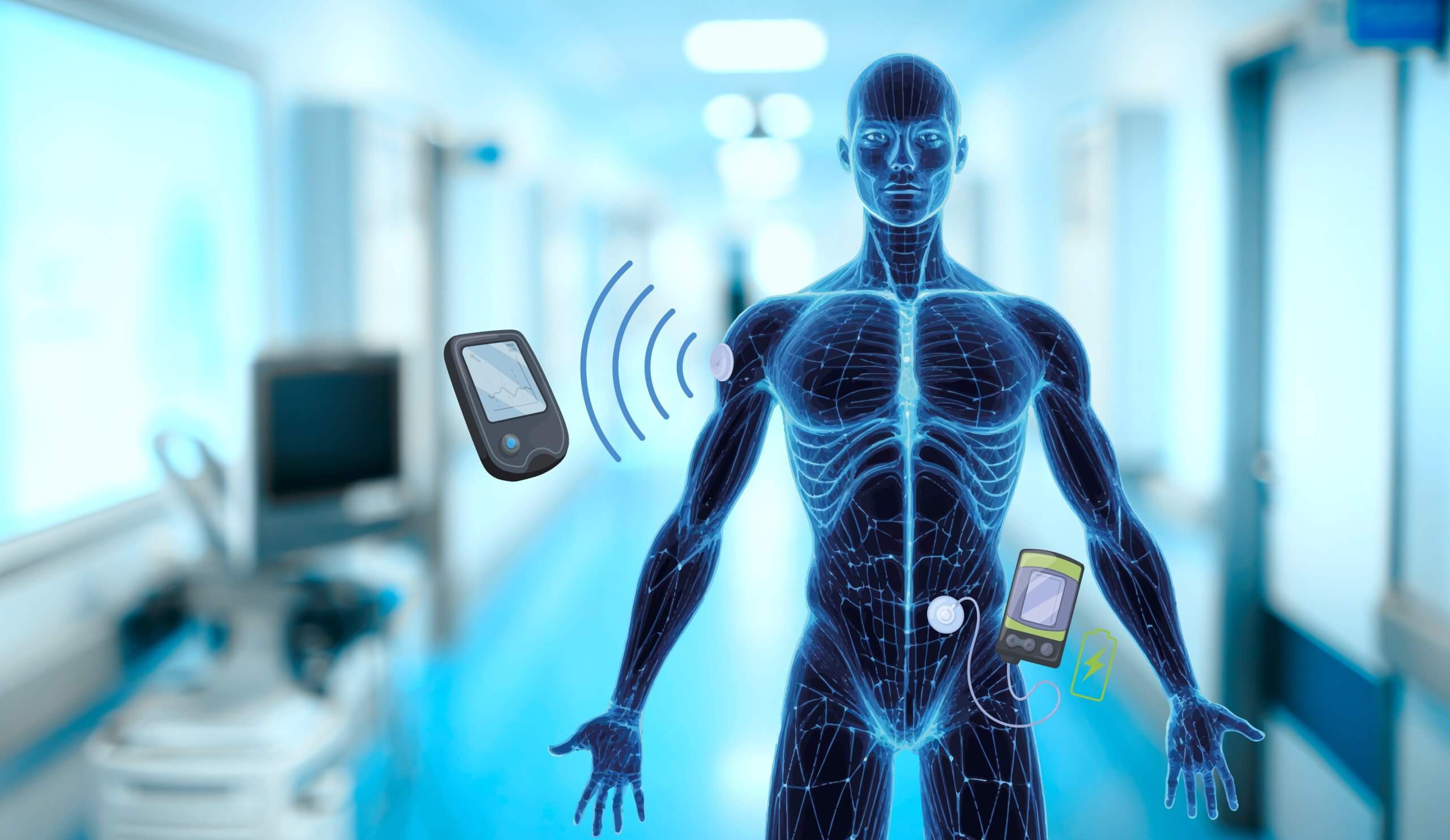
Users of the insulin pump must continue to measure their blood glucose several times a day. However, this is no longer necessary if a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) device is used. Such a device measures the glucose level automatically at regular intervals of a few minutes and can also be connected to an insulin pump.
A CGM system consists of a biosensor with a transmitter unit. This sends the data for continuous monitoring of the glucose level to the data collector, the receiving device.
Biosensor:
A small sensor is inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen or upper arm. This sensor measures the glucose content in the tissue fluid approximately every five minutes.
Transmitter:
The sensor is connected to a transmitter that transmits the measured glucose values wirelessly to a receiving device or an app on a smartphone. In accordance with a manufacturer-specific transmission standard the determined glucose content is transmitted via Bluetooth, NFC or .
Receiving device:
The receiving device, which is attached to the abdomen or the outside of the arm, displays the wirelessly transmitted glucose values in real time and can trigger alarms if the glucose values are too high or too low. The receiving device can also be a smartphone or smartwatch. It is also possible to send the values to an insulin pump, which can react to the fluctuations accordingly.
Long-life batteries for a continuous power supply to the insulin pumps and CGM systems
For diabetics, it is essential that their supportive devices work reliably and without interruption. This is exactly where Jauch’s long-life lithium batteries come into play, which have been specially developed for use in medical devices such as insulin pumps and CGM systems.
The sensors in CGM systems use non-rechargeable batteries. Lithium button cells from Jauch are available in various sizes and pin configurations and are characterized by high energy density and reliability.
The receivers also require a stable and reliable energy source. Lithium polymer or lithium ion batteries from Jauch, equipped with a battery management system, are ideal here. Lithium polymer batteries are available in various shapes and sizes and enable a flexible design of the receiver. Lithium ion batteries offer a large selection of cells and, thanks to their high energy density, enable a compact design of the insulin pump or the CGM system’s receiving device.
Precise control of insulin delivery thanks to the stable frequency of the Jauch frequency products
In addition to the batteries, Jauch’s frequency control products also play a decisive role in insulin pumps, CGM systems and receiver devices.
Precise time measurement
Reliable pulse generators are essential for the measurement, control and precise timing of insulin delivery. Jauch crystals and oscillators provide stable and accurate frequencies that enable precise control of insulin delivery. This is particularly important to ensure the exact dosage of insulin and thus guarantee the health of the user.
Watch crystals such as the JTX110 from Jauch enable precise time measurement throughout diabetes management. Jauch’s high-precision kHz crystals and oscillators ensure accurate tracking of these readings without the risk of deviations.
Precise dosing
As already described, a CGM system comprises a biosensor and a transmitter unit that continuously transmits measured values via Bluetooth or NFC to a data collection device to monitor the glucose level. This device then determines the insulin dose to be delivered.
Miniature crystals from Jauch’s JXS series, such as the JXS10 or JXS11, serve as clock generators for the wireless communication unit, which transmits the measured values from the biosensor. They ensure that the Bluetooth or NFC connection remains stable and reliable by providing a precise and temperature-stable frequency. The high frequency stability and low ESR value of the JXS crystals ensure stable and accurate data transmission. This is particularly important to ensure that the glucose readings are sent correctly and without delay to the data collection device equipped with a JXS21, for example.
The following applies to all applications involving reliable insulin monitoring: developers must be aware of all factors that can lead to frequency deviations. The sum of all worst-case scenarios of these factors must not exceed the limits of the application.
Jauch has developed frequency control products that function particularly reliably in the field of medical technology. These components are ideal for use in wireless and network applications that require a smaller tolerance budget. The so-called WA crystals (WA = wireless application) are artificially pre-aged in temperature chambers during production. As a result, they only experience greatly reduced ageing of a maximum of +/-7ppm over 10 years.
Jauch also offers a wide range of oscillators and (VC)TXCOs for the special requirements of WiFi and mobile phone connections in diabetes management.


 Deutsch
Deutsch